[最も欲しかった] s p d f orbitals 3d 161837-3d structure of s p d f orbitals
The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atomsThere are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental) Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals In the n=1 shell you only find s orbitals, in the n=2 shell, you have s and p orbitals, in the n=3 shell, you have s, p and d orbitals and in the n=4In the second electron shell, n = 2 The 2s and 2p orbitals have one node In the third electron shell, n = 3 The 3s, 3p, and 3d orbitals have two nodes, etc Types of Node There are two types of node radial and angular The number of angular nodes is always equal to the orbital angular momentum quantum number, l

A An Atomic Orbital Has N 3 What Are The Possible Values Of L And M B List The Quantum Youtube
3d structure of s p d f orbitals
3d structure of s p d f orbitals-Letter s p d f g h The subshell with n=2 and l=1 is the 2p subshell;Any orbital which is partially filled (thus excluding s 2, p 6, d 10 and f 14 orbitals) obtains a certain magnetic moment, as there is an inequality between occupied spinup and spindown electrons


An Atomic Model Our Present Model Of The Atom Is Based On The Concept Of Energy Levels For Electrons Within An Atom And On The Mathematical Interpretation Of Detailed Atomic Spectra The Requirements For Our Model Are Each Electron In A Particular Atom
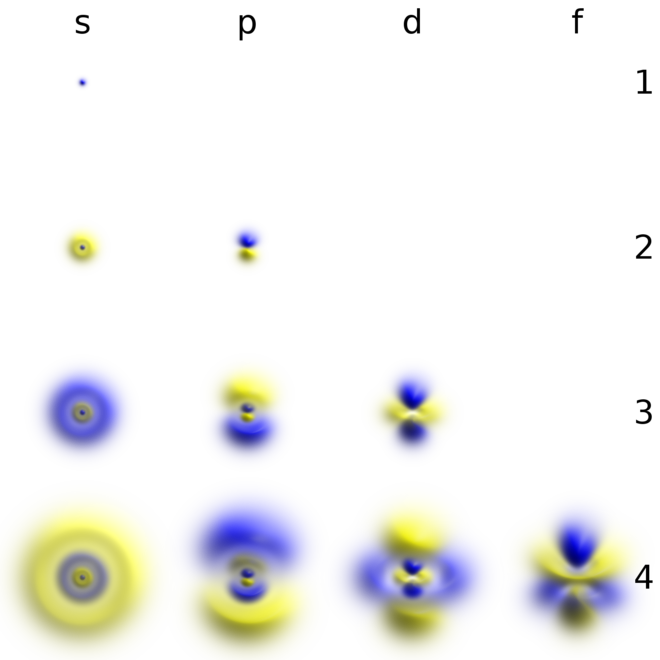
The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively These names, together with the value of n , are used to describe the electron configurations of atomsFor a p orbital, draw a figure eight;S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;
Here you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termiHow Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!"s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!
Footnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellS orbitals only have 1 orientation in space p orbitals can have 3 orientations in space d orbitals can have 5 orientations in space f orbitals can have 7 orientations in spaceFor a d orbital, draw a fourleafed clover;


Shells Subshells And Orbitals Video Khan Academy



Solved Write The Electron Configurations For The Followin Chegg Com
A s orbital _ 2__ b the subshell of p orbitals __ 6___ c the subshell of d orbitals _ 10 __ d the subshell of f orbitals__ 14 __ e the subshell of g orbitals__ 18 __ 10 How many electrons can inhabit all of the n=4 orbitals?P x yz plane p y xz plane p z xy plane Case III When = 2, 'm' has five values 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It implies that d subshell of any energy shell has five orbitals The shapes of all d orbital is not identical Shapes of these Four d orbitals are same d xy, d yz, d xz, Shape of dorbitals It implies that d subshell has 5 orbitals ieThere is only one 4s orbital and there are 5 3d orbitals the 4s orbital is spherical the 4s orbital has a lower energy the 3d orbitals have a lower energy 17 Which of the atom pairs both have only three unpaired electrons in their d orbitals?


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
There is 3d till 5d ( 3d , 4d ,5d ) There is only 4f (4f) QuestionsWhats the difference between s,p,d,f?Contains five electrons in its 3d orbitals Manganese In bohr's model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located?The answer is provided by the formula 2l 1, where l takes different values depending on whether we are speaking of s, p, d or f orbitals For s orbitals l = 0, for p orbitals l = 1, for d orbitals l = 2 and so on As a result there is potentially one s orbital, three p orbitals, five d orbitals, seven f orbitals and so on for each shell The flaw


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model



Chemical Bonding Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Britannica
For an s orbital, draw a circle;Arrange the following orbitals in order of increasing energy 3p 5d 2s 4s 4f 3d from CHEMISTRY 101 at Neuqua Valley High SchoolS, p, d and f orbitals are possible 6 Which one of the following statements is correct?


Electron Configurations
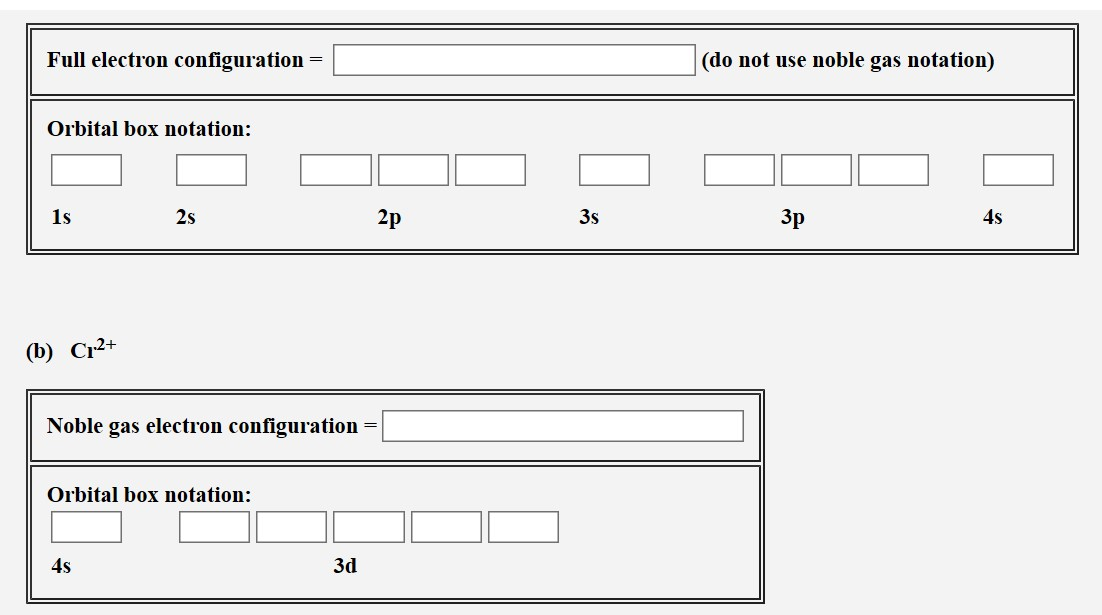


Solved Write The Electron Configurations For The Followin Chegg Com
All five 3d orbitals contain two nodal surfaces, as compared to one fo\(r\) each p orbital and zero fo\(r\) each s orbital In three of the d orbitals, the lobes of electron density are oriented between the x and y, x and z, and y and z planes;Fred Senese of Antoine Frostburg explains "You might expect that the 's' stands for 'spherical' and 'p' stands for 'polar' because these imply the shapes of the s and p orbitals, but unfortunately, the letter designations have nothing to do withIntroductory chemistry students often have difficulty visualizing the 3dimensional shapes of the hydrogenic electron orbitals without the aid of physical 3D models Unfortunately, commercially available models can be quite expensive 3D printing offers a solution for producing models of hydrogenic orbitals 3D printing technology is widely available, and the cost of 3D printing "inks" is


Virtual Orbitals 3d Chemistry Apps On Google Play


Molecular Structure Atomic Orbitals
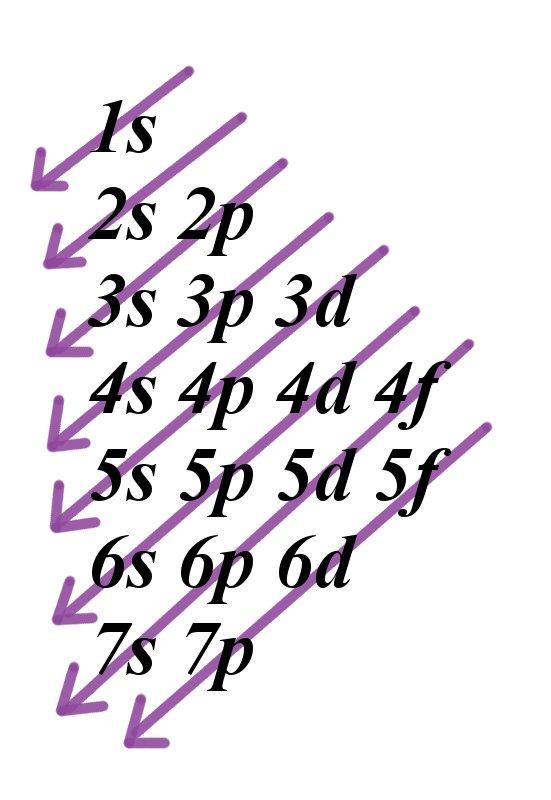
3d yz 3d x2y2 3d z2 ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 4 HYBRID ATOMIC ORBITALS sp sp orbitals are a combination, or hybrid, of an s and a p Showing the p orbitals Showing the s and p orbitals ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11 CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2The 3d structure of two orbitals of an atomIf n=3 and l=0 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f It is not necessary to memorize this listing, because the order in which the electrons are filled in can be read from the periodic table in the following fashion superscript to indicate how many


An Atomic Model Our Present Model Of The Atom Is Based On The Concept Of Energy Levels For Electrons Within An Atom And On The Mathematical Interpretation Of Detailed Atomic Spectra The Requirements For Our Model Are Each Electron In A Particular Atom


F Orbitals The Delocalized Physicist
Orbitals can be ranked in the increasing order of orbital energy as follows 1s < 2s = 2p < 3s = 3p = 3dAn electron configuration shows the electrons distribution by sublevel using the quantum numbers n and l, where the notation for l is by its letter designation (s, p, d, f, etc) For example, the notation 3d 4 indicates 4 electrons in the d sublevel (l=2) of the n =3 principal energy level You are referred to Chapter 7 in the textbook where aD and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are a total of


18 Electron Cloud Models


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
Fred Senese of Antoine Frostburg explains "You might expect that the 's' stands for 'spherical' and 'p' stands for 'polar' because these imply the shapes of the s and p orbitals, but unfortunately, the letter designations have nothing to do withThese orbitals are referred to as the \(3d_{xy}\), \)3d_{xz}\), and \(3d_{yz}\) orbitals, respectively3d yz 3d x2y2 3d z2 ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 4 HYBRID ATOMIC ORBITALS sp sp orbitals are a combination, or hybrid, of an s and a p Showing the p orbitals Showing the s and p orbitals ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11 CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2



Atomic Orbital S P D 3d Real Youtube
/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
How Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!Footnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellS < p < d < f The energy levels of 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals are different even though they belong to the same shell n = 3 However, it may be noted that the energy of electrons in the same orbital is the same


Types Of Orbitals Mr Banks Fav Student
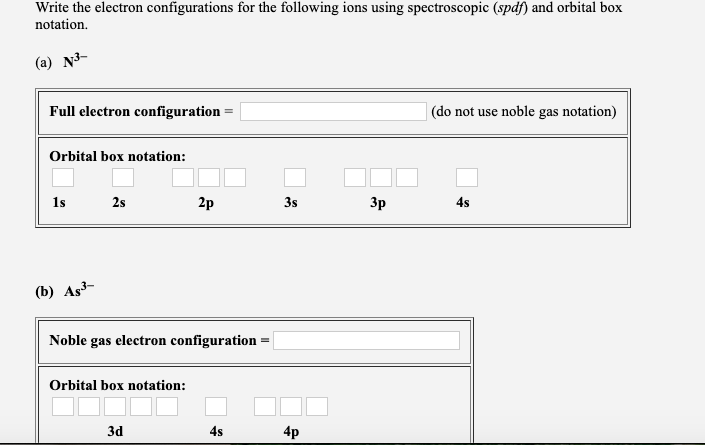


Solved Write The Electron Configurations For The Followin Chegg Com
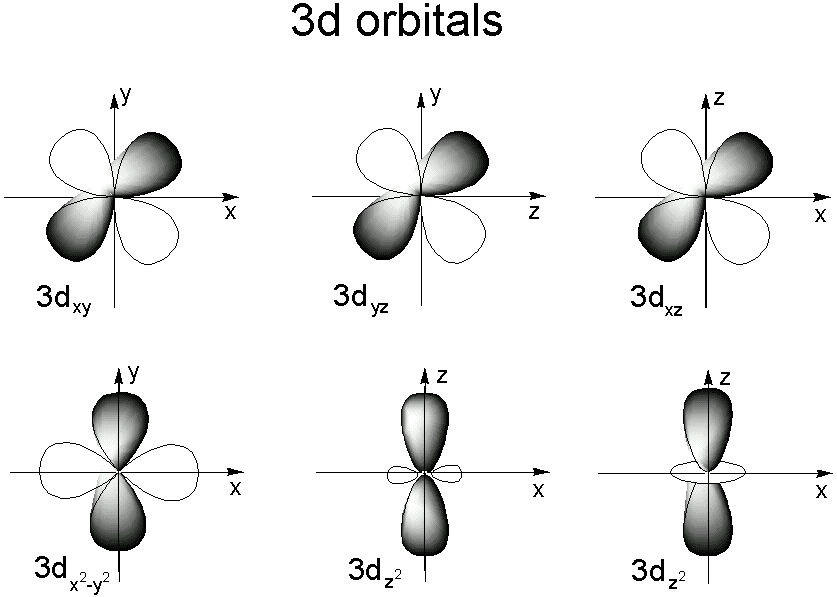
For example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2 and 3d z 2 The d xy , d yz and d zx orbitals have same shape ie, clover leaf shape but they lie in XY, YZ and ZX planes respectivelyThe d z2 orbital is symmetrical about Zaxis and has a dumb bell shape with a doughnut shaped electron cloud in the centreThe overlap situation becomes extreme when the forbitals are added to the s/p/d sum The general forbital set is used in the figure Of note is the change in the number of lobes required to accommodate a pair of electrons 1 for 2, 7 for 8, 25 for 18, and ~64 for 32 along with a few tori4s = 2 4p = 6 4d = 10 4f = 14 32 Total Electrons
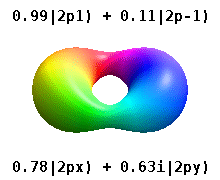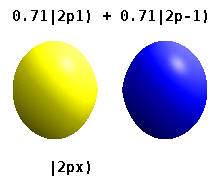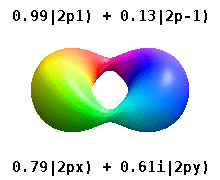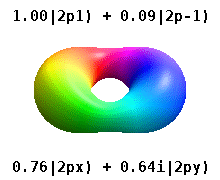


Atomic Orbital Wikipedia



Orbitals Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Multiple Choice Practice Problems Youtube
Shape of sorbitals in 3D CONTROLS An illustration of the shape of the 1s, 2s and 3s orbitals The s sub shell can hold a maximum of two electrons as there is only one orbital S orbitals are spherical in shape and increase in size as the energy level or shell increasesWriting Electron Configurations The distribution of electrons among the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configurationThe electrons are filled in according to a scheme known as the Aufbau principle ("buildingup"), which corresponds (for the most part) to increasing energy of the subshells 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5fMaximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitals Maximum 14 electrons in 7 orbitals


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
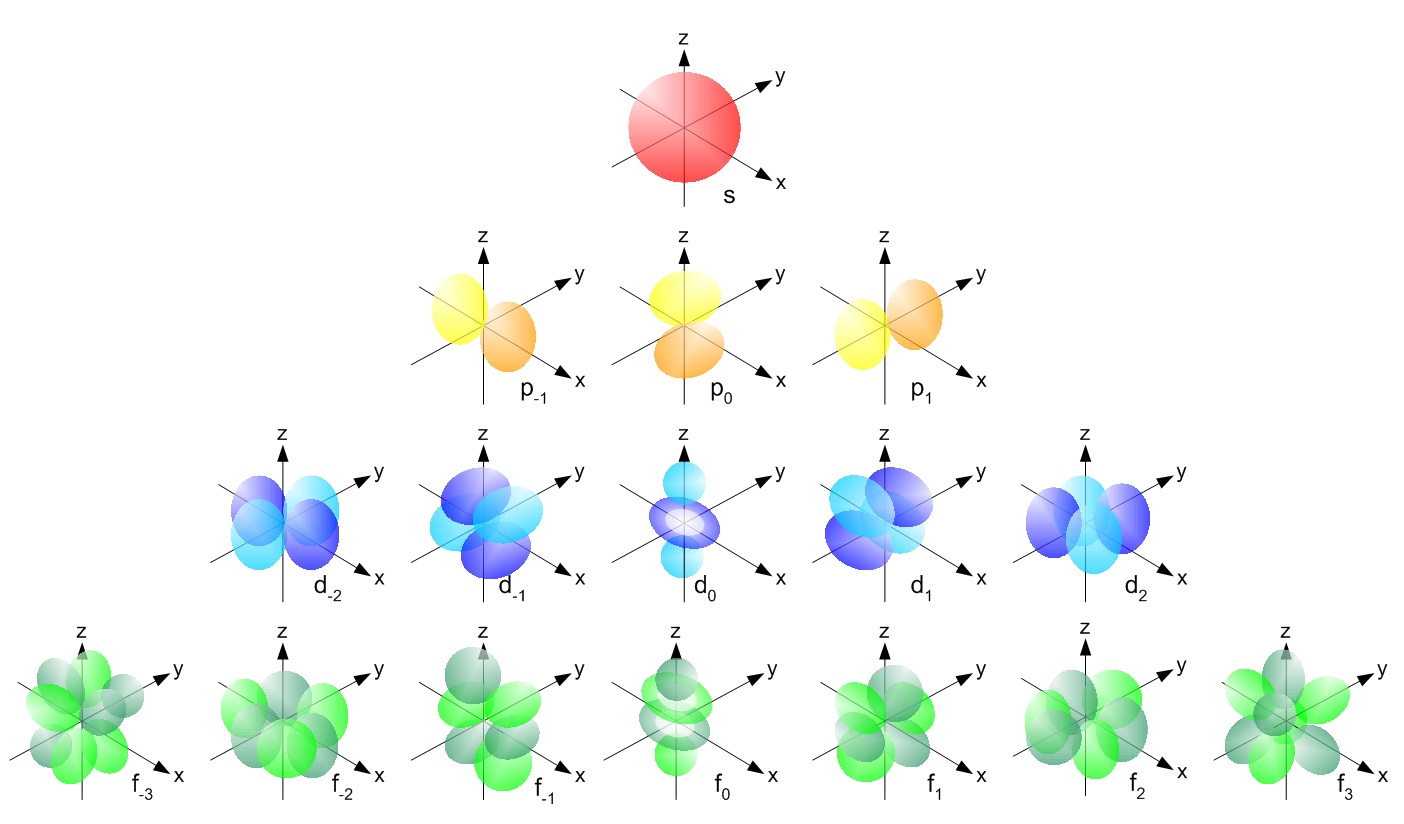


12 9 Orbital Shapes And Energies Chemistry Libretexts
Here you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termiOrbital Shapes (s, p, d and f) Explanation The proposed tetrahedral nucleus structure , along with rules for proton spin alignment that is the cause of the repelling force used to calculate orbital distances , can explain the shapes of the s, p, d and f orbitals2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


Electron Configuration Chart



Dublin Schools Lesson Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configurations
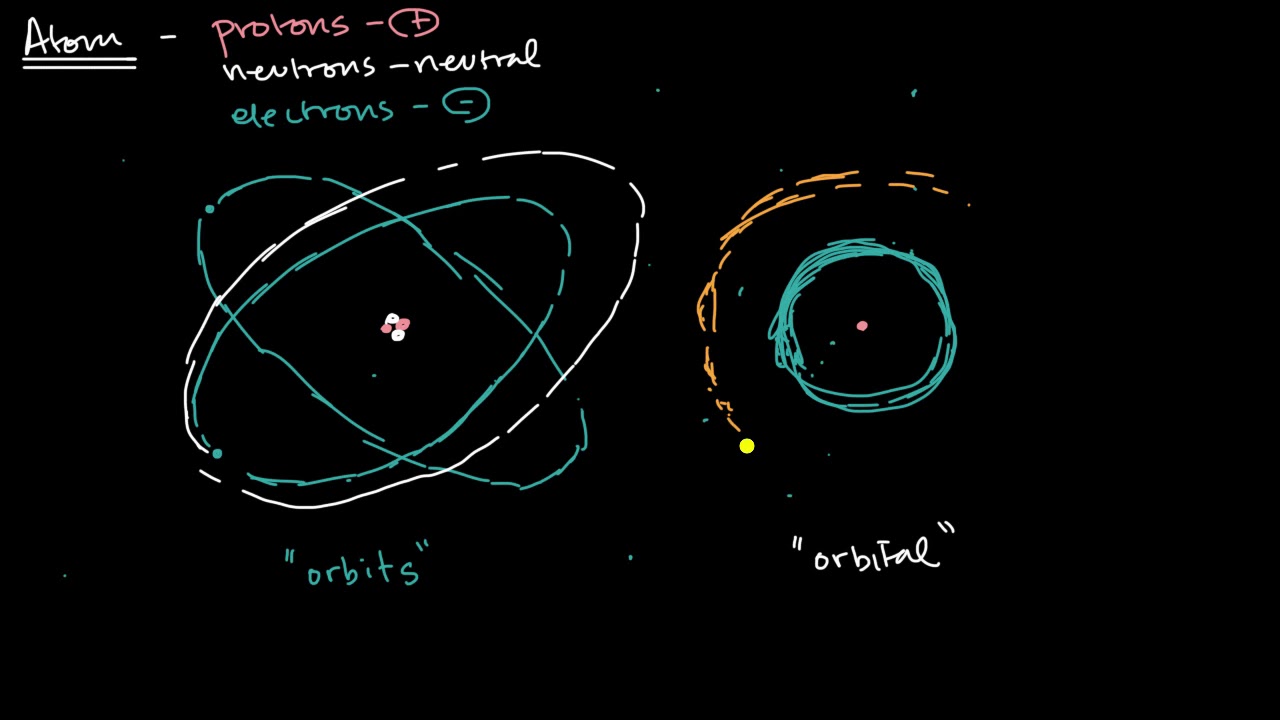
Now, you'll also hear the term, subshell, subshell, or sometimes people will say sublevels and that's where they're talking about s or p or d and eventually f so if I circle this, I'm talking about that first shell Now, the first shell only contains one subshell and that's the 1s subshell and the 1s subshell only has one orbital( is it the number of electron each can carry if so then how much does each carry or is it the location )If I say 3s ( 1 orbital) what does it mean?If I say 4f ( 7 orbitals ) what does it mean?"s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Shapes Of S P D F Orbitals Stlfinder
For an f orbital, see below An s orbital is a sphere In two dimensions, we draw it as a circle A p orbital consists of two lobes of electron density on either side of the nucleus We usually draw p orbitals as figure eights, but we should remember p orbitals are really muchIndicate the number and type (s, p, d, f) of orbitals in each of the following a 4p sublevel b 3d sublevel c n = 3 Determine the number ofa Electrons than can occupy one p orbital b P orbitals in the 2p sublevel c D orbitals in the n = 4 energy level d Electrons than can occupy the 4f sublevel( is it the number of electron each can carry if so then how much does each carry or is it the location )If I say 3s ( 1 orbital) what does it mean?If I say 4f ( 7 orbitals ) what does it mean?



Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
Because the order of electron penetration from greatest to least is s, p, d, f;Each sublevel has differing numbers of orbitals Sublevels are designated with lowercase letters Sublevel s contains one orbital, p contains three, d has five, f has seven, g has nine, h has 11 and i has 13D zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;



Chemistry Online 13
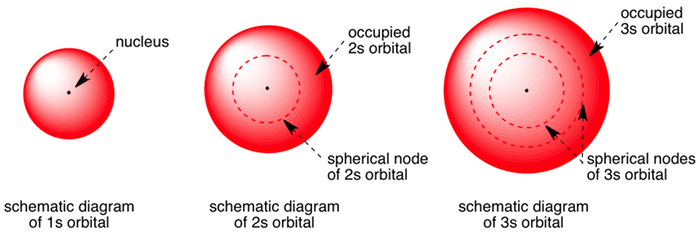


Shape Of S Orbitals In 3d
A) the electrons move around the protons, which are at the center of the atom p and d only c) s, p, d only d) s, p, d, and f c) s, p, d only What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p?The order of the amount of shielding done is also in the order s, p, d, f Since the 2s electron has more density near the nucleus of an atom than a 2p electron, it is said to shield the 2p electron from the full effective charge of the nucleusOrbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry Learn more about atomic orbital at Byjus
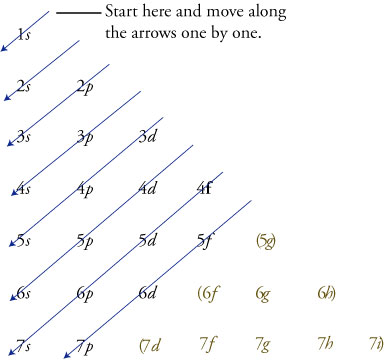


Electron Configurations



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
Shapes of Orbitals and Electron Density Patterns The s orbitals are spherical, while p orbitals are polar and oriented in particular directions (x, y, and z) It may be simpler to think of these two letters in terms of orbital shapes (d and f aren't described as readily)However, if you look at a crosssection of an orbital, it isn't uniformAt the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3px, 3py, 3pz) At the third level there are a total of nine orbitals altogether The five 3d orbitals are called 3dxy 3dxz 3dyz 3dx² y² 3dz² To make sense of the names, we need to look at them in two groupsHere you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termi
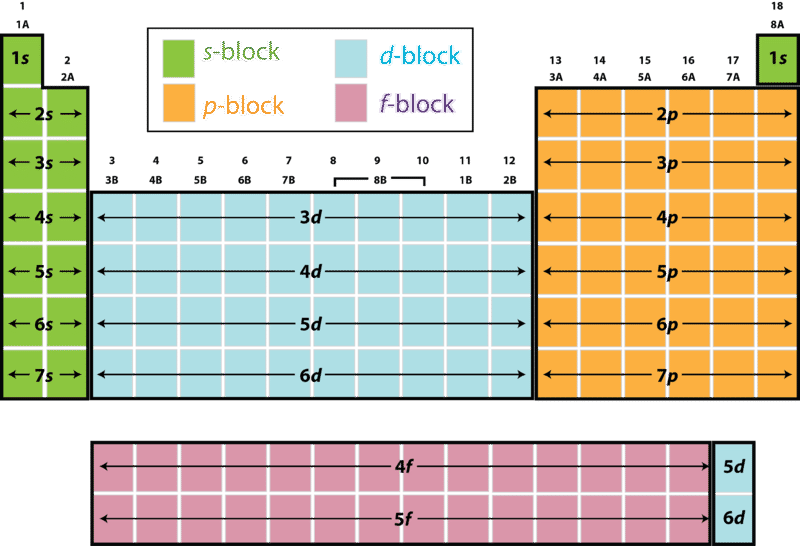


Electron Configuration And The Periodic Table Ck 12 Foundation


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau
Click the images to see the various 3d orbitals There are a total of five d orbitals and each orbital can hold two electrons The transition metal series is defined by the progressive filling of the 3d orbitalsThese five orbitals have the following ml values ml=0, ±1, ±2,There is 3d till 5d ( 3d , 4d ,5d ) There is only 4f (4f) QuestionsWhats the difference between s,p,d,f?Maximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitals Maximum 14 electrons in 7 orbitals
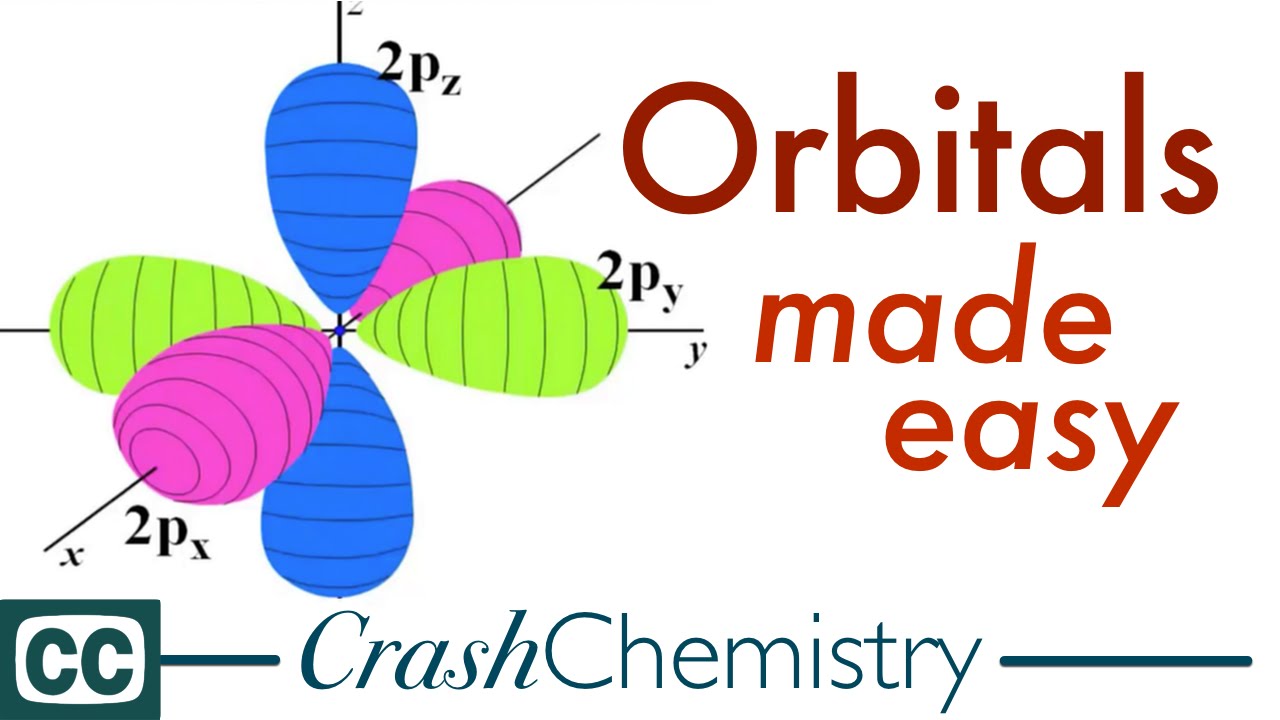


Orbitals The Basics Atomic Orbital Tutorial Probability Shapes Energy Crash Chemistry Academy Youtube



Electron Orbitals S P D Youtube
Rules Firstly, the electrons are arranged into a sequence of groups in order of increasing principal quantum number n, and for equal n in order of increasing azimuthal quantum number l, except that s and p orbitals are kept together 1s 2s,2p 3s,3p 3d 4s,4p 4d 4f 5s, 5p 5d etc Each group is given a different shielding constant which depends upon the number and types ofHow Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!



Atomic Orbitals Physics In A Nutshell


What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Uncategorized The Delocalized Physicist



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


The Order Of Filling 3d And 4s Orbitals



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange


Virtual Orbitals 3d Chemistry Apps On Google Play
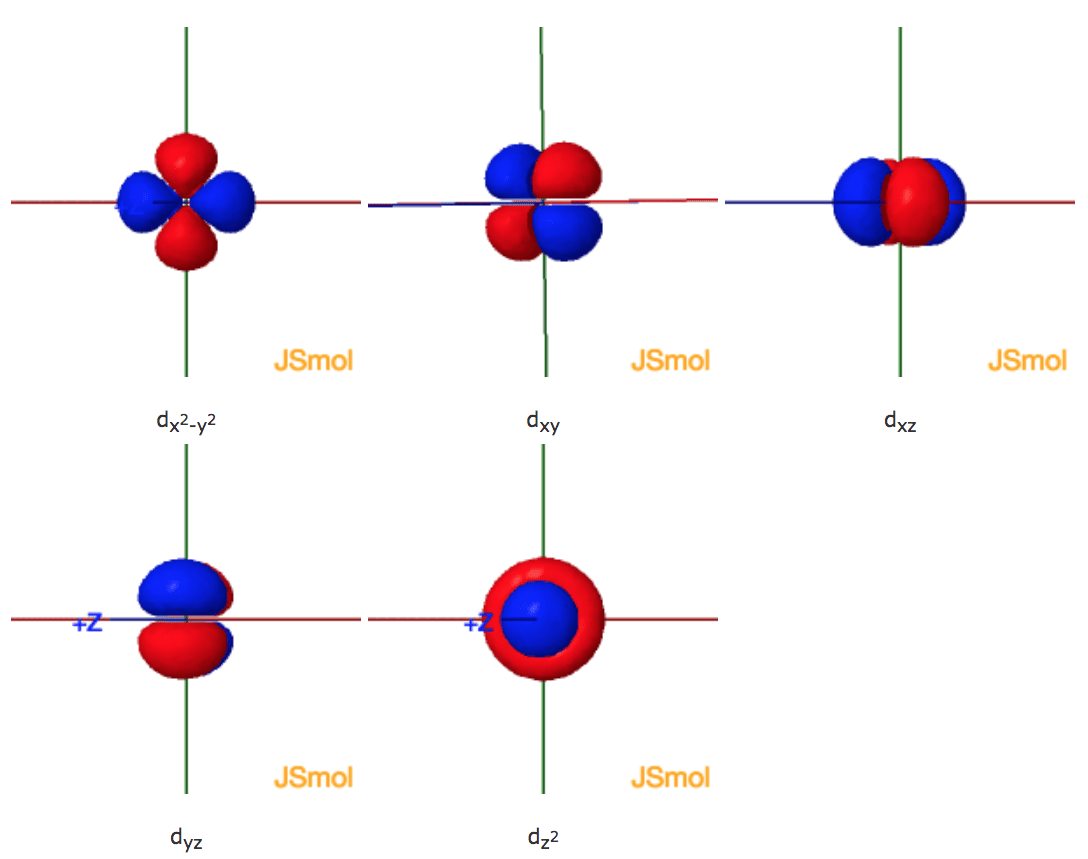


Shapes Of The 3d Orbitals In 3d



A An Atomic Orbital Has N 3 What Are The Possible Values Of L And M B List The Quantum Youtube



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ShellAtomicModel-5a6ab592aded4bb7a1328f809e4f10da.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates And Superpositions Png Wikimedia Commons


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model



Orbitals Diagram For Spdf Quantum Numbers In High School Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes



S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



Atomic Orbital Wikipedia


Visualizing Electron Orbitals


Diagram Database Just The Best Diagram Database Website
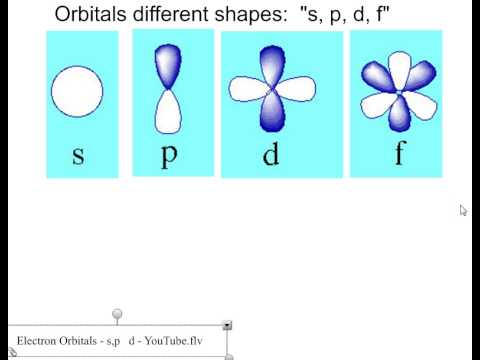


Quantum Model And Spdf Orbitals Youtube



D Orbital Photos Royalty Free Images Graphics Vectors Videos Adobe Stock



Shapes Of Orbitals Spdf Stlfinder


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic
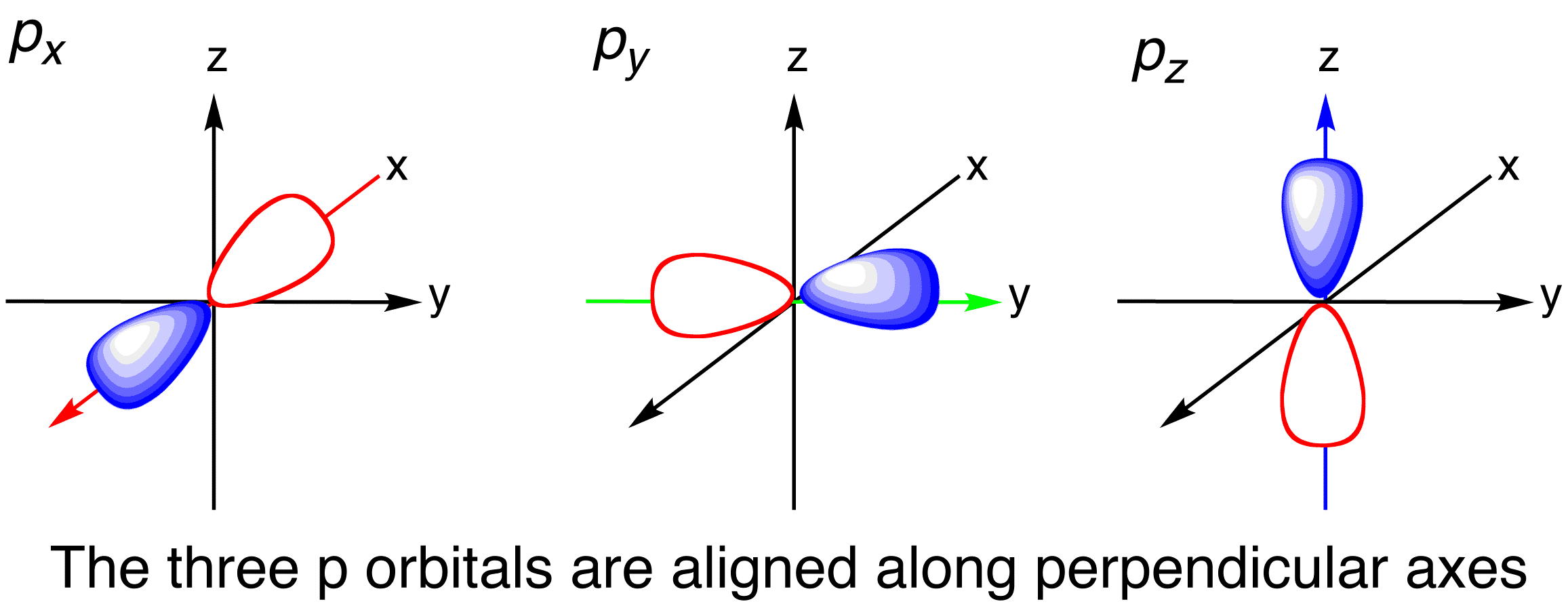


Shape Of P Orbitals In 3d


Electron Configuration Wikipedia


Q Tbn And9gcqqfx6pzmsxdi2uw9vzetjpauxulquptk5uk642sgjdu4qcc5vw Usqp Cau


The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education


Ch 9


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau


1 2 Atomic Structure Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Atomic Orbital Wikiwand


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
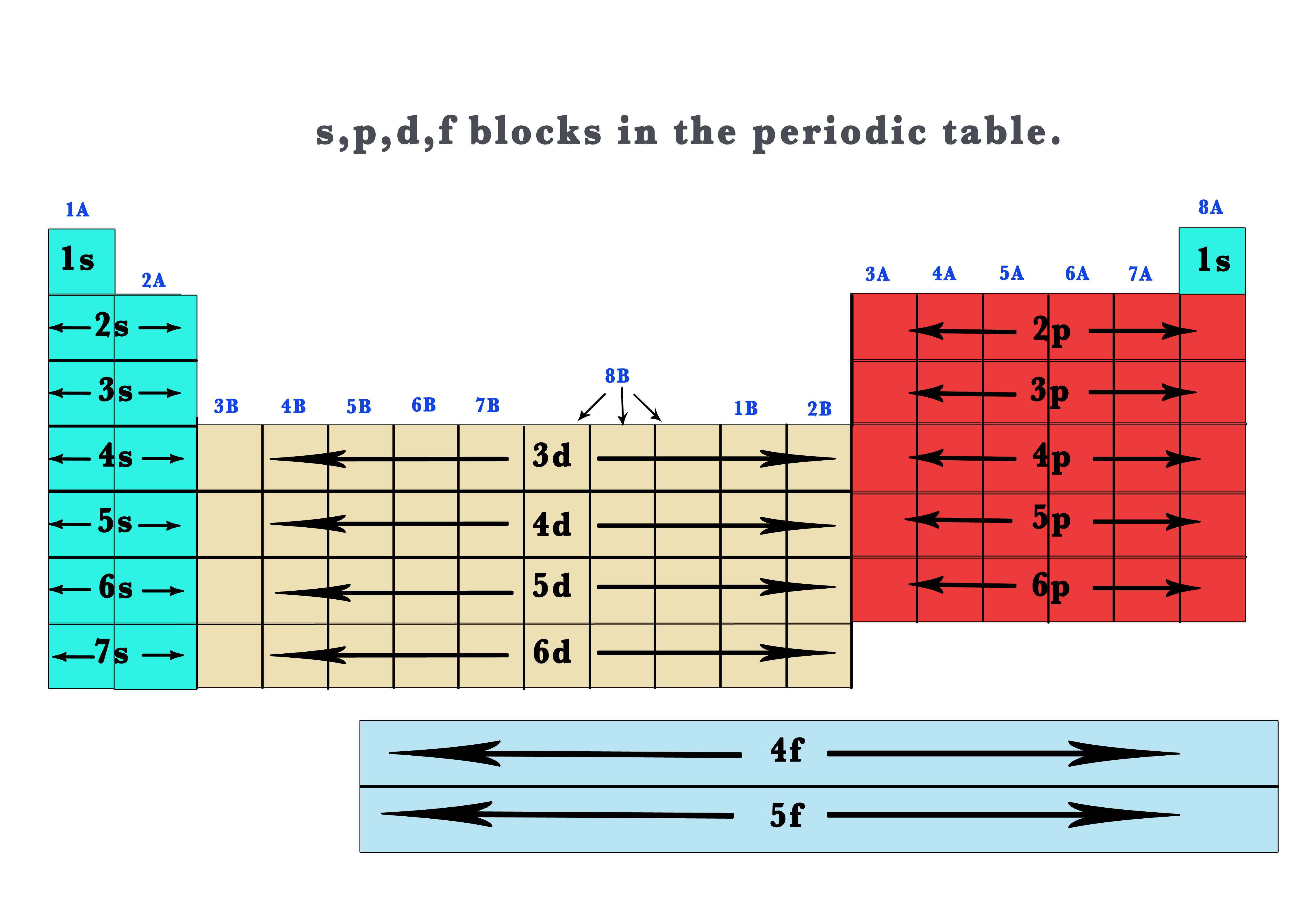


41 The Periodic Table S P D F Blocks Madoverchemistry Com
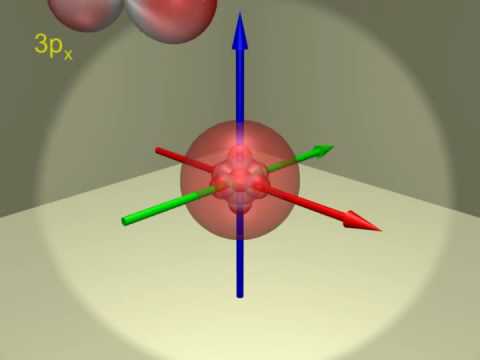


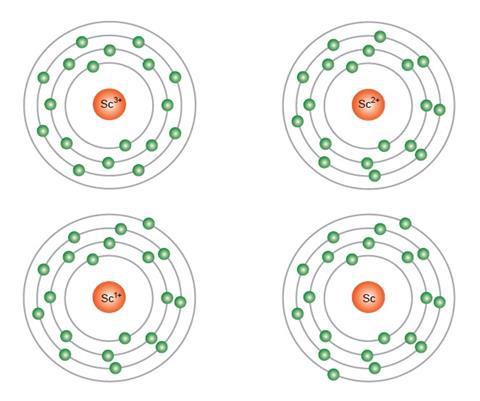
Atomic Orbitals Electron Configuration Of Scandium Z 21 Youtube
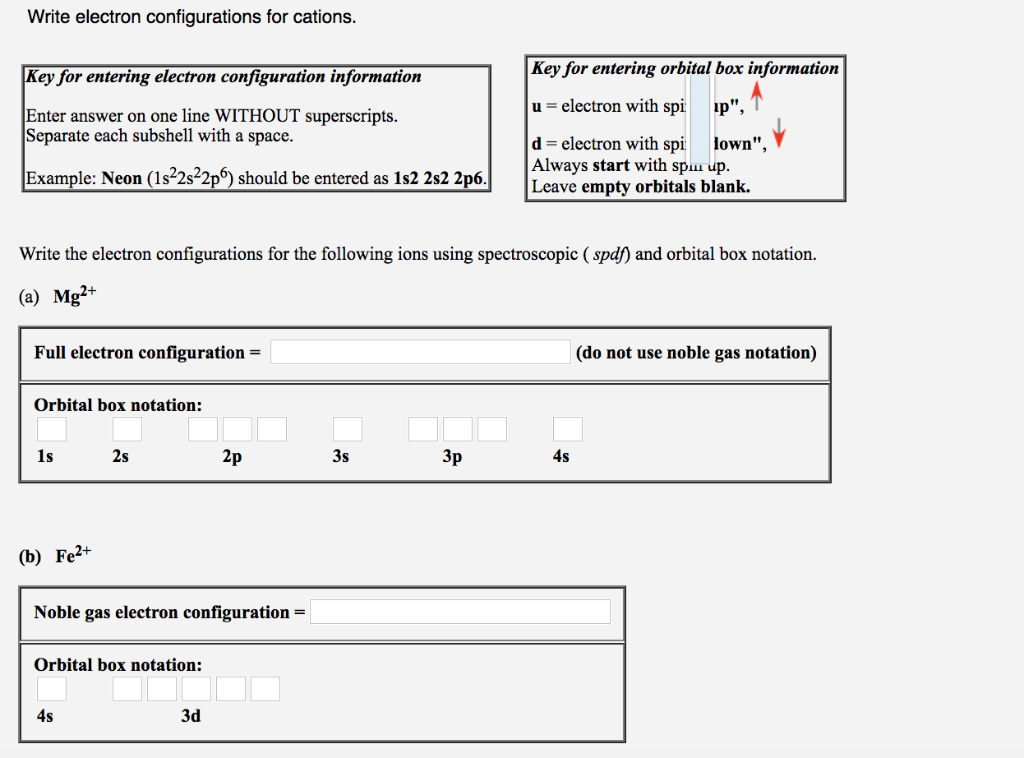


Solved Write The Electron Configurations For The Followin Chegg Com


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Virtual Orbitals 3d Chemistry Apps On Google Play


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model



Quantum Number Wikipedia



The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates Mpositive Png Wikimedia Commons


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic
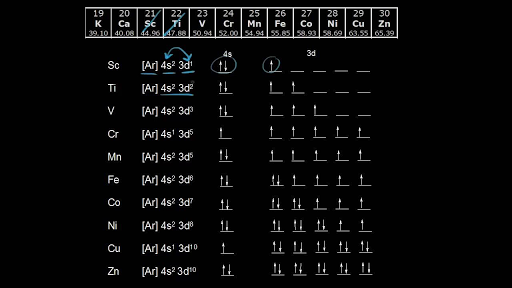


Electron Configurations Of The 3d Transition Metals Video Khan Academy


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
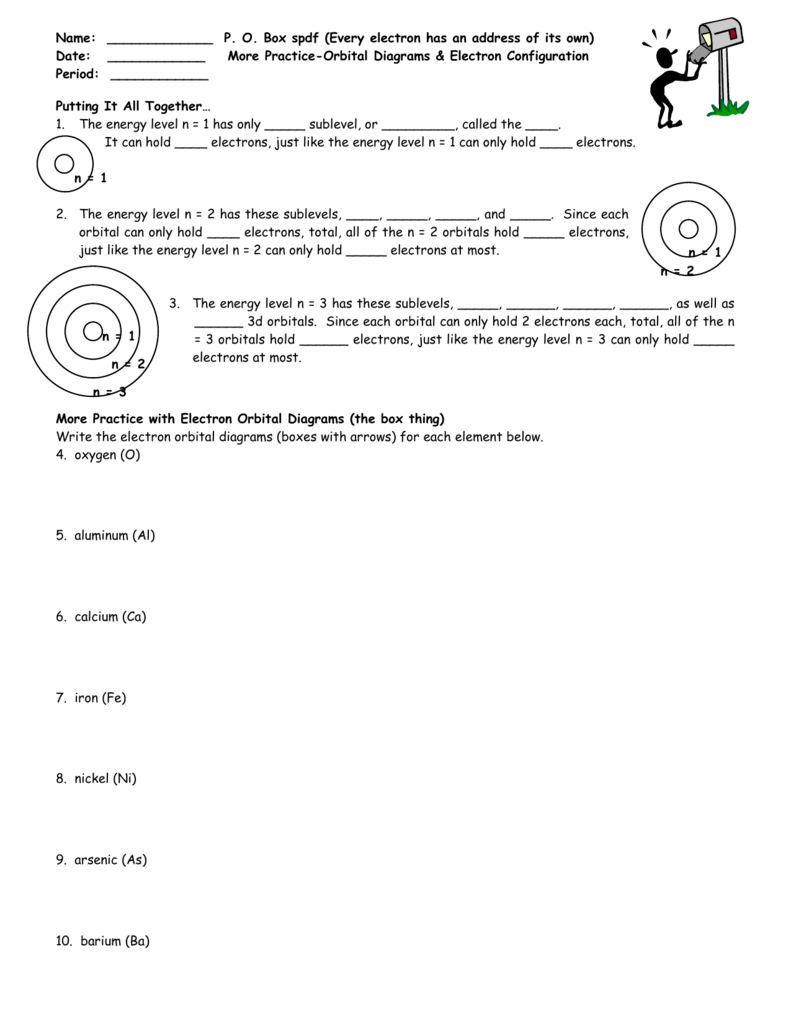


Po Box Spdf Worksheet
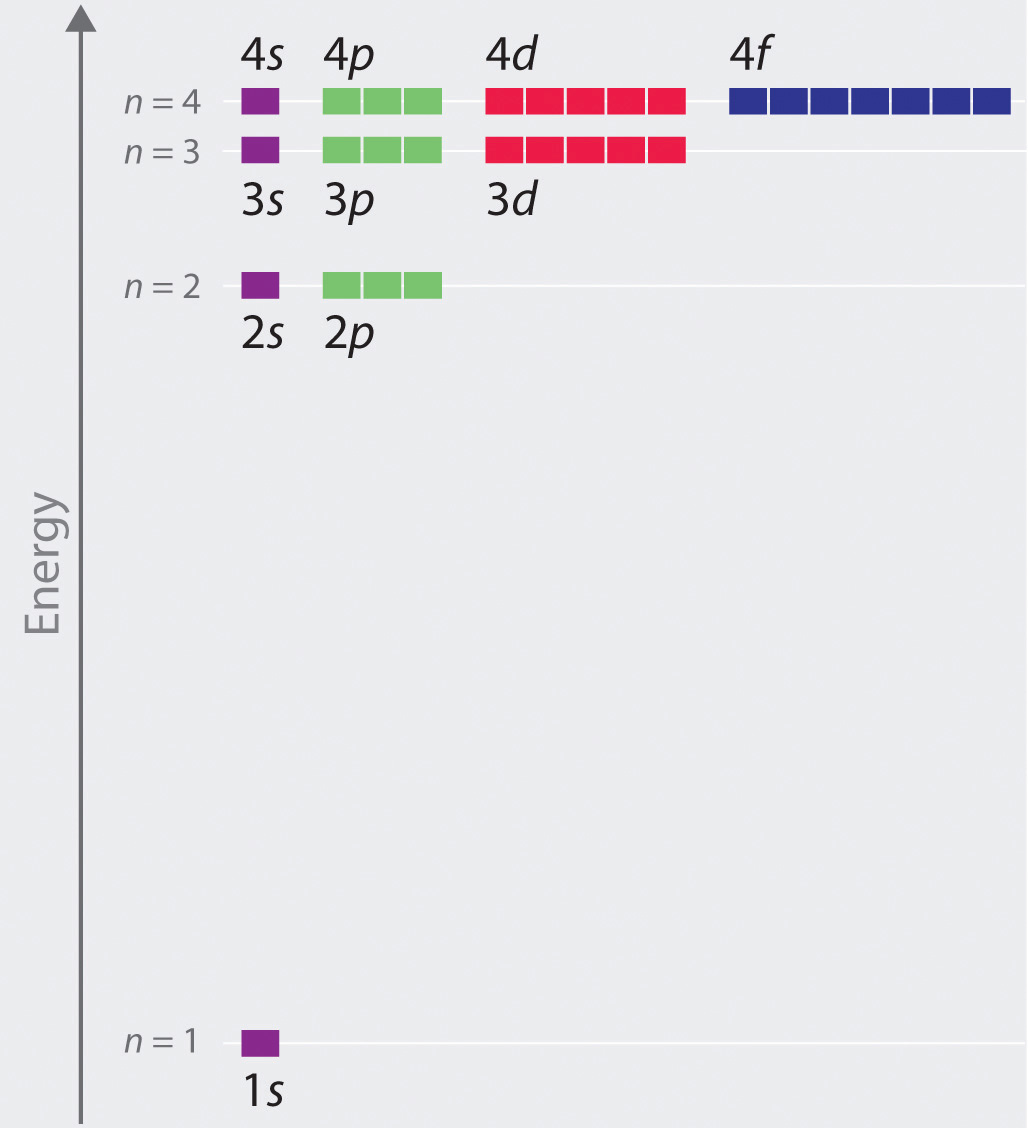


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Virtual Orbitals 3d Chemistry Apps On Google Play


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Plz Explain The 3d Shaped Of The Spdf Shells The Content Above Is Not Clear Chemistry Structure Of Atom Meritnation Com


Shells Subshells And Orbitals Video Khan Academy
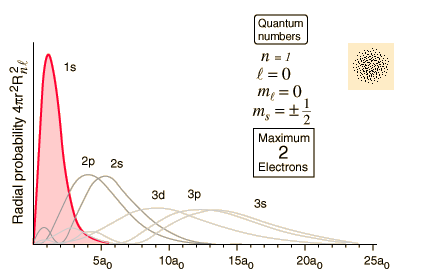


Orbitals



Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube


Electron Configurations


Q Tbn And9gcthkbfxsvcmd3slqsueqeacalyhgywzqc Gx3p0kkc4ifvl6ry Usqp Cau
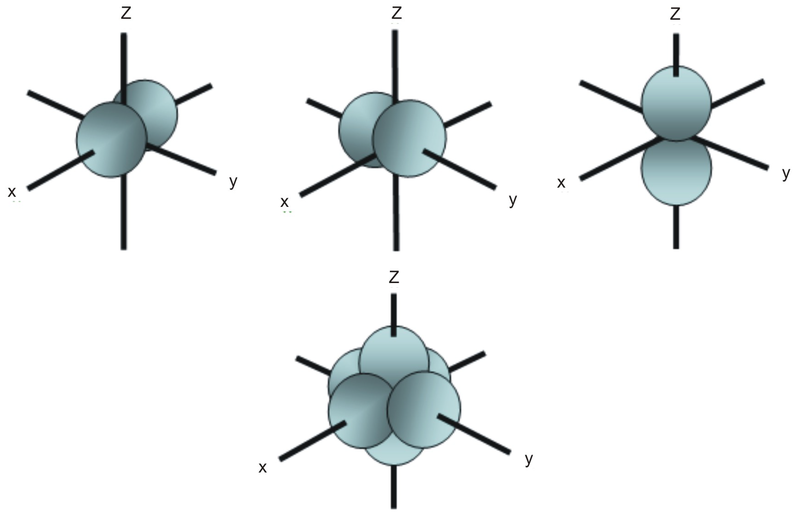


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
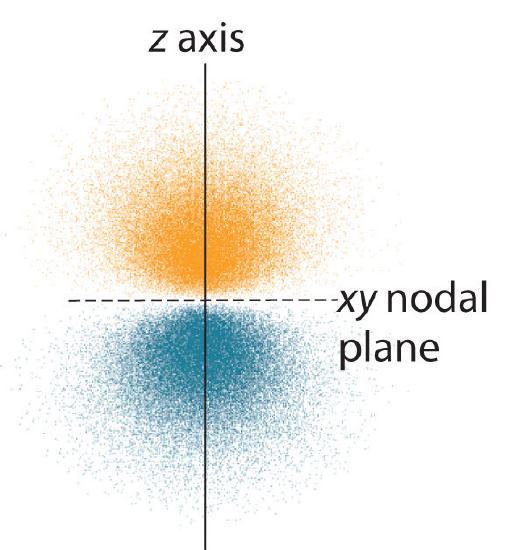


6 6 3d Representation Of Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
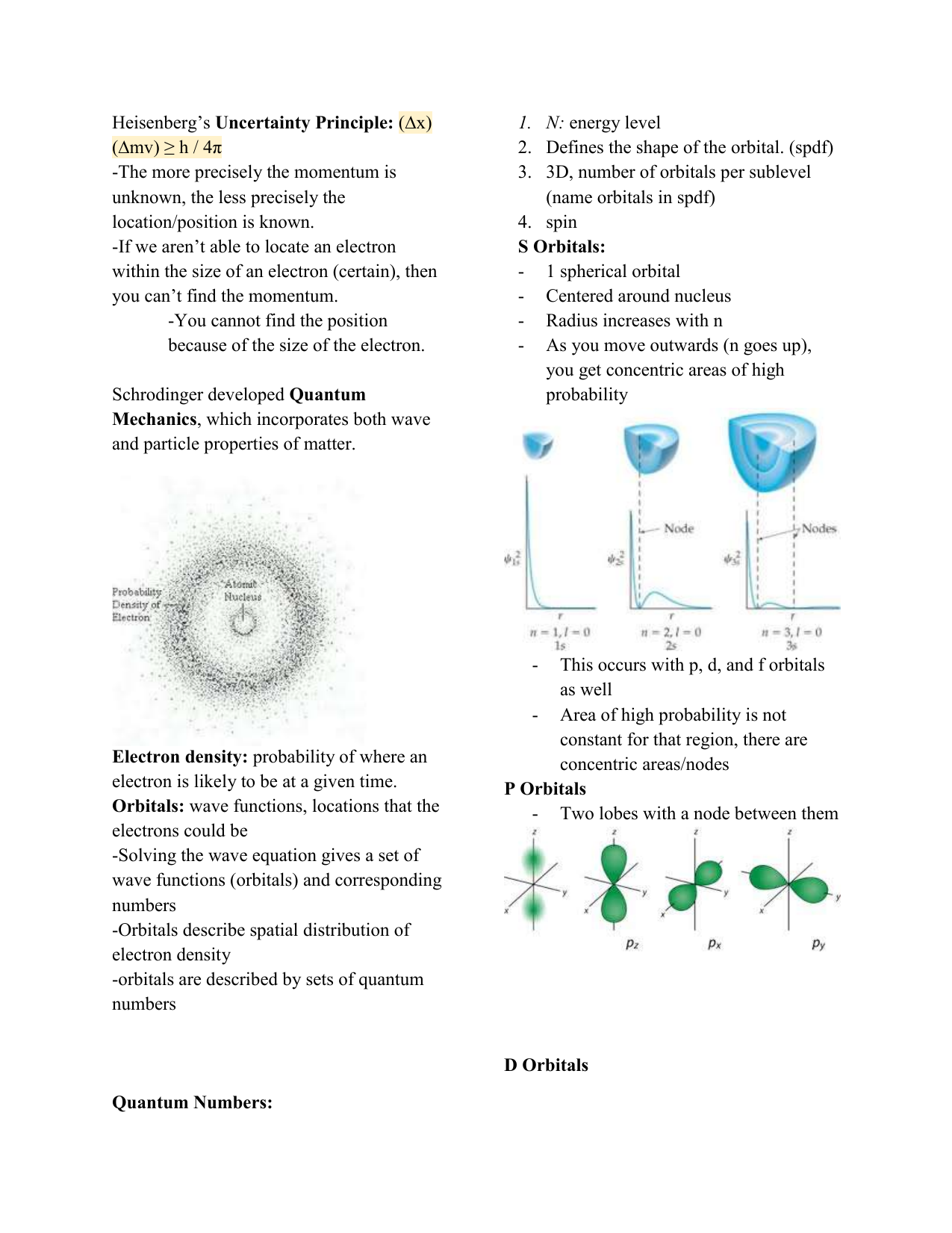


Ap Chem Notes 6 4 6 6 In Class
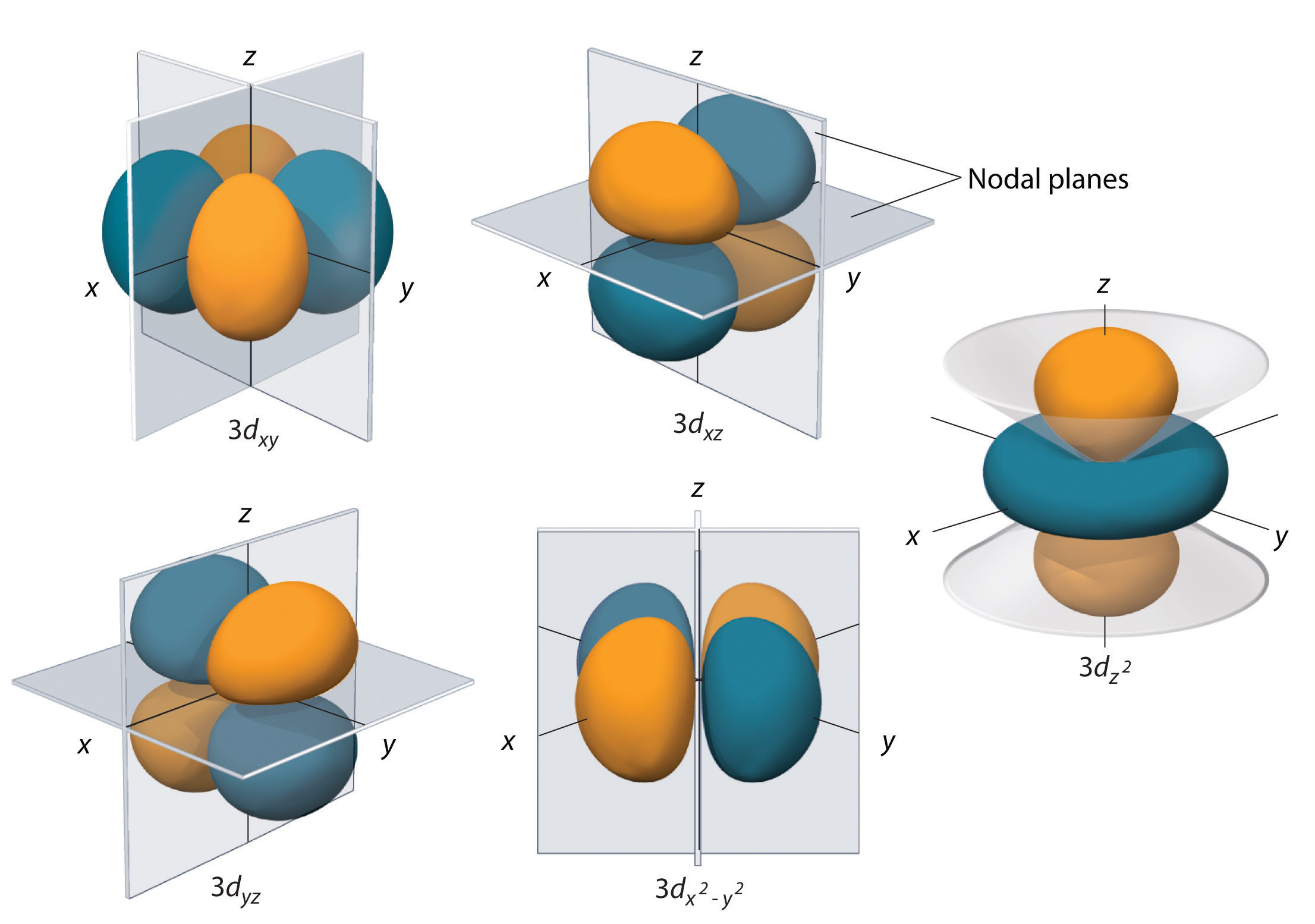


6 6 3d Representation Of Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts



Electron Orbitals Introduction To Chemistry


コメント
コメントを投稿